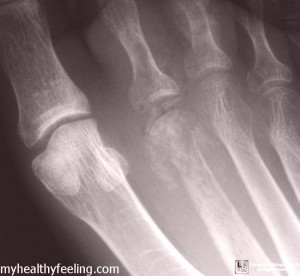
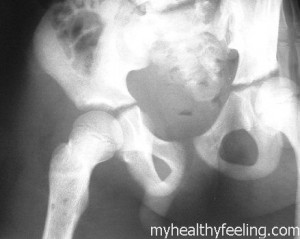
The term Osteomyelitis is used to refer to the infection caused in the bond. There are infections that may reach to the bone by traversing by the mean of blood stream or may also spread through nearby tissues. This condition may also directly infect the bone if there is any injury experienced that also exposed the wound to harmful viruses or germs. In case of children, this condition is commonly noticed at longer bones around the upper arms as well s legs. However, in adults this condition in usually found in vertebrae or bone that makes the spine. People with preexisting diabetes mellitus are also at risk of developing this physical adversity if they are affected by foot ulcer. This condition was once said to be incurable but due to advancement of medical industry it can be successfully treated now.
Symptoms of Osteomyelitis:
There are certain signs and symptoms that may be experienced by a person affected with Osteomyelitis. These symptoms may include:
• Fever or increased body temperature
• Irritation
• Lethargy experienced by young children
• Pain experienced at the region of infection
• Redness, protrusion and warmth over the region of infection
These are chances that a person afflicted with this condition may not see any signs or symptom and the condition may remain nondescript. But incase you experience any of the aforementioned symptoms, it is crucial to consult you doctor immediately.
When to consult your doctor?
It is essential to see you doctor as soon as you experience any of the aforementioned sigs or symptoms. However, even if you experience that a persistent mild bone pain as progressed along with prevalence of fever, then doctor’s assistance serves as a significant aid. There are possibilities that you may be at risk of developing infectious condition related to bone due to surgery or medical regimen, if you suspect any such physical changes then consult your doctor immediately.
Causes of Osteomyelitis:
Majority of Osteomyelitis cases are determined to be caused due to a bacteria known as staphylococcus, which is a kind of germ that is usually found in the nasal passage of the individual. These germs may also enter the bone and cause such bone related issues. Here some modes in which these germs can enter the bone:
• Through the Blood stream:
Germs from pneumonia and UTI or Urinary tract infection or other parts of the body may enter into your blood streams and travel to a weakened region in your bone. In case of children, Osteomyelitis has its influence on softer regions known as growth plates, at either of the ends of the long bones of arms as well as legs.
• From infected wound:
Serious puncture and wounds may also carry these germs deep inside your body. If such a serious wound becomes infected, the germ can also spread into a nearby weakened bone.
• Direct contamination:
Direct contamination may happen when a bone if fractured severely and a portion of the bone is penetrating your skin. Direct contamination may also afflict an individual who undergoes joint replacement surgery or fracture repair.
Drugs and treatment for Osteomyelitis:
There are several treatment techniques that can be adopted to treat Osteomyelitis. One of the commonly used treatments for this condition includes antibiotics or other invasive (surgical) treatment. This surgery is mostly done to remove a part of bone that is infected or is dead
Medicines:
A comprehensive bone biopsy will help in understanding the kind of germs that are causing the infection. This will help you doctor to understand what kind of antibiotic will be best suitable to treat the particular type of infection. These antibiotics are often given to the patients intravenously at their arm for a regimen of 6 weeks. There are possibilities that you may also suffer from some side effects which may include vomiting, queasiness as well as diarrhea.
Surgical procedures:
When other medical treatments do not work then surgical treatments are suggested to the patients. There are different kinds of surgeries recommended to the individuals suffering from Osteomyelitis, which may depend on the severity of the condition. These techniques may include:
Draining the infected region:
In this process your doctor may try to drain away the accumulated pus around the affected bone region. He may create an incision near the localized infection and clean away the foul fluid which carries the infection.
Affected bone and tissues removal:
There is a procedure named as debridement wherein the doctor operating on the affected region tries to take away as much affected bone as possible, taking a minute margin of unaffected bone to make sure that the infected region have been taken away completely. Any tissues that shows any sign of infection is also removed.
Restoring blood circulation to bone:
After the debridement your doctor may also try to fill up the empty remaining space with a piece of bone or healthy tissues. For example he may derive skin or muscles from other region of your body. In some cases temporary fillers are used to cover the pocket until he finds you healthy enough to undergo tissue or bone grafting. The grafting procedure enables you body to repair and restore damages blood vessels and develop ne bone.
Taking away foreign object:
in some cases the issue may arise due to foreign objects like supportive screws or surgical plates installed during earlier surgery; hence, such objects may have to be eliminated.
Amputation:
Amputation is a procedure wherein the affected body region is removed from the body. This is the last option that the surgeon may suggest. When no other treatment works, amputation is suggested in order to prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of the body.
These surgical treatments are usually followed by a regimen of antibiotics that prevents any further infection. These antibiotics are often administered through intravenous mode of administration. In general cases the bone is resistant to infection, but in case any abnormalities your bone may become vulnerable. It is essential to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any symptoms of Osteomyelitis as mentioned above.