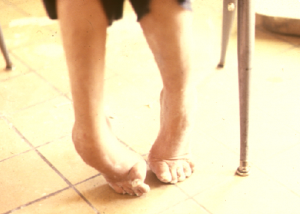
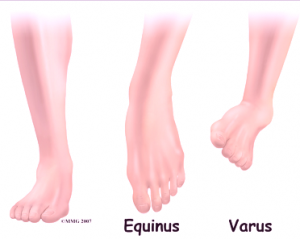
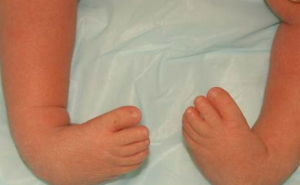
Club foot is a birth defect wherein there are abnormalities, irregularities or deformities of the foot. The abnormality may affect only one foot or both the feet.
When an individual is born with club foot, the foot is twisted or distorted one way or the other. The foot is usually placed a sharp angle with the ankle. This may result in the affected individuals walking with an unusual gait, more often either on the heels or the sides of the feet.
Club foot may result in developmental delays in walking, as the child may find it very difficult to walk in the beginning. However, club foot is not a serious disorder and can be treated easily.
Symptoms of club foot
- Club foot is visible in symptomatic abnormalities of the foot.
- In club foot, the upper part of the foot may turn sideways or downward and towards the inside. This may increase the arch and turn the heel inward. Severe cases of feet affected by club foot may result in giving the affected foot the appearance of a golf club, or one that is turned upside-down.
- In addition, the calf muscles of the affected foot may not develop fully.
- The affected foot usually tends to be a little shorter than the normal foot.
- Club foot does not result in any pain or discomfort, though if left untreated can cause increased peer ridicule or embarrassment
- Club foot can result in serious complications with the progress of age. It increases the risk to develop arthritis in children
- The child may face increased difficulties in walking due to the fact that one foot is smaller than the other. This may make the child walk with an unusual style or an awkward gait. The child may not be able to walk on the soles and may end up walking on the balls of the feet or the sides of the feet or even the feet in extreme cases. Such compensatory measures can lead to the development of boils, calluses or sores on the feet as well as ill-formed calf muscles
- It is important that club foot is treated at the earliest to avoid physical, emotional and psychological disorders in the future
Causes of club foot
- Club foot is idiopathic in nature. It has no known causative factors. It is a known fact that the position of the fetus does not lead to the development of club foot. However, theories increasingly suggest the presence certain conditions such as spina bifida or congenital irregularities of the skeleton can lead to club foot. Spina bifida is a dangerous birth defect that results due to the inadequate closure of the tissue that surrounds the spinal column of the fetus.
Some of the risk factors for the development of club foot include the following:
- The male gender is at increased vulnerability to develop club foot
- Club foot has a genetic basis and therefore a family history of club foot increases the risk to develop the disorder
- Instances of smoking during pregnancy increase the risk to develop club foot. A woman who has a family history of club smokes during pregnancy then the chances of the baby being born with the birth defect are twenty times greater than average.
Tests and diagnosis of club foot
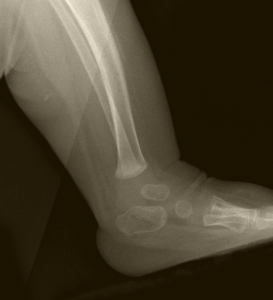
- There are no specific tests to determine the presence of club foot as it is clearly visible after birth. However, a doctor may conduct an x-ray, to determine the severity of the deformity
- Club foot can also be diagnosed before birth with the help of an ultrasound. This is more so if club foot has affected both the feet. The treatment for club foot has to wait till after birth, but an early diagnosis can assist the parents in gathering relevant data and advice for its effective treatment.
Treatment of club foot
Treatment for club foot focuses on correcting the deformities before the child is able to learn to walk. This is possible because the bones of the child are very flexible.
Some of the treatment and preventive methods of club foot are listed below:
- The Ponseti method that involves stretching and casting procedures: In this method the foot is manipulated into a correct position. After that it is placed in a cast to maintain that position. This may go on for many weeks. Once the repositioning and recasting has resulted in a realignment of the foot, there are several procedures that are followed. Stretching exercises, nocturnal splinting with braces as well as special footwear is prescribed for nearly three years to maintain the correction of the foot. Regular visit to the doctor is necessary during this period to prevent any relapse
- The French method that involves stretching and taping: In this method the foot is manipulated into the correct position and then taped with adhesive tapes. This method is conducted on a daily basis for up to two months. After that the sessions are reduced to three times a week till the child is six months old. After the correction of the deformity, special exercises and nocturnal splints are used to maintain the correction of club foot.
- In severe cases of club foot that does not respond to non-surgical methods of treatment, surgery of the affected foot may be required to correct the deformity
- Club foot cannot be completely prevention. However, avoidance of smoking environments as well as quitting smoking during pregnancy, avoidance of alcohol and drug use can decrease the risk of the baby developing club foot.
Club Foot Pictures
Check out pictures of club foot to see how the feet are deformed or rendered abnormal