How is pulmonary embolism treated? First of all we need to understand the cause and risk factors of this disease.
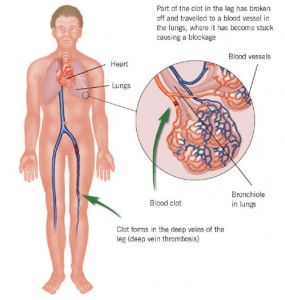
Pulmonary embolism is the sudden obstruction of a major artery in the lung, that is caused by blood clot. In many cases, these clots may be small and not so harmful but they are powerful enough to damage the lung. If the clot is big and stops blood flow to the lung, it can cause more problems. So, there is a need for prompt pulmonary embolism treatment or there can be more problems.
Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms
Pulmonary embolism symptoms can be in the form of
1. Cough that can be in the form of pink colored mucus
2. Shortness of breaths
3. Nagging chest pain that gets worst when you cough or take a deep breath.
4. Fast heart rate, palpitations
5. Too much sweating
6. Feeling giddy
7. Feeling anxious
Pulmonary Embolism Causes
The main reason for pulmonary embolism is a blood clot in the leg that cuts loose and moves to the lungs. If this clot in a vein is near the skin, it may not be threatening. However, if these blood clots are in a place where deep veins are located, it can cause pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary Embolism Risk Factors
Here are the factors that are at risk for pulmonary embolism:
1. People born with blood that tends to clot quickly
2. Sedentary lifestyle, sitting in bed for a long time after recuperating after surgery, sitting in front of the computer for a long time, sitting in a car or flight for long trips.
3. Severe infection, cancer, stroke, heart failure
4. Pregnancy, child birth mostly due to cesarean
5. Hormone therapy , taking birth control pills
6. Smoking
7. Old age more than 70 years or being extremely overweight or obese.
Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis
The symptoms of pulmonary embolism are similar to those of heart attack, pneumonia, panic attack etc, so diagnosis can be difficult. The doctor will first do a physical examination and ask questions about your past health, symptoms etc that may help him arrive a conclusion if you have pulmonary embolism or not. Some of the tests that are used include spiral CT Scan, MRI, ultrasound, blood tests, MRI, ECG, EKG etc.
Pulmonary Embolism Treatment
The first line of treatment for pulmonary embolism is with medicines known as anticoagulants. These are known as blood thinners that prevent new clots and do not let the old clots grow. One blood thinner that is quite effective which doctors give, is known as heparin. They will also prescribe warfarin, a blood thinner in the pill form. Though people have to take it for a few months, the ones with high risk for clots may have to take it for the rest of their lives.
There are other clot fighting drugs for pulmonary embolism treatment like thombolytics that can be given. These medications can dissolve clots quickly but they can also cause serious bleeding issues. There is a surgery known as embolectomy that can remove blood clots.
If blood thinners are not working as a part of the pulmonary embolism treatment, then the doctor may have to put a filter into the vena cava(large vein) that carries blood from the lower parts of the body to the heart. Then this vena cava filter can stop blood clots from coming to the lungs.
In case, you have been affected by pulmonary embolism once, there are chances that you may contract it again. Blood thinners can reduce the risk but the risk of bleeding can be there. So, if your doctor prescribes a blood thinner, you have to understand how to take it and also go for regular blood tests.
Prevent Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism prevention is possible if you do not allow blood clots to form in your legs. This can be done by doing the following things
1 Avoid sitting in one place for long periods of time, go for a walk every hour or so. Do leg exercises.
2 If you travel a lot, make sure that you drink a lot of fluids. Avoid caffeinated drinks and alcohol
3 If you take blood thinners, take them the way your doctor advises you to do