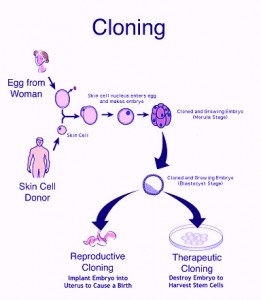
Therapeutic cloning is a process which involves the stripping a fertilized egg of its nucleus and replacing it with the nucleus from other cells. Such eggs are the reproduced as embryos and the stem cells from such embryos are used to produce new organs and tissues. The stem cells are also useful in treating a number of medical conditions and illnesses such as cancer, Parkinson’s disease, etc. However the field of therapeutic cloning is a controversial one and has caused much debate over the years. This is because the embryo tends to die on most of the occasions.
The history of therapeutic cloning
In November 2001, the scientists and researchers from Advanced Cell technology based in Massachusetts announced the use of cloned embryos in the advancement of therapeutic research. A fertilized egg that has all its genetic material removed was inserted with a skin cell. The egg subsequently divided leading to the creation of therapeutic cloning technology. California became the first state in the United States to legalize the process of therapeutic cloning of an embryo, and a year later, in 2003, Britain became the first country that issued research licenses that enabled the creation of stem cells through the process of human embryonic cloning.
The debate surrounding therapeutic cloning
Most groups, who are against abortion, believe that life starts at conception and since therapeutic cloning leads to the destruction of embryos, they have constantly stood against the use of this technology. Such groups also believe that the insertion of cells into fertilized eggs leads to the creation of a human life. The removal of the stem cells from such embryos results in the death of such human life. It is debated that the killing of one life form to save another is not justified.
Therapeutic cloning pros
An organ that is created by the use of therapeutic cloning has miniscule chances of organ rejection during transplant, because it is created as an exact match of the patients DNA. This would also mean that there would be no need for an organ donor as well as no surgery for the removal of the organ from the donor. Also, there is no need for the patient to wait for the donor’s death before receiving the required organ. Thus therapeutic cloning has many valuable uses and can be used for the treatment of several diseases that are very difficult to treat. The subject of therapeutic cloning is also benefits the field of medical research as scientists can effectively learn and understand the method of organ regeneration.
Therapeutic cloning cons
Therapeutic cloning is dependent on the stem cells that are extracted from embryos due to the fact that adult cells are few and limited in number. Only a few parts of the stem cells that are extracted are usable. Other cells may mutate and result in tumors in the recipients. Additionally, in order to be able to cure any disease, there is a requirement for millions of eggs. The supply of eggs is limited and increasing the supply would mean subjecting women to many experiments which would be harmful for them. Thus, despite the varied uses of therapeutic cloning, its many cons have prevented it from becoming the premier mode of treating diseases.