What is vasculitis ?
The swelling of the blood vessels is referred to as vasculitis. It could happen to anyone, male or female, regardless of age. With vasculitis, the affected blood vessels become inflamed, thickening the walls, thus resulting to the abnormal flow of blood to the tissues and organs. In some cases, the blood vessel would totally shut causing serious injury to the affected organ or tissue due to lack of oxygen and blood supply. There are also cases of vasculitis that give rise to aneurysm because the wall of the blood vessel has weakened. The actual cause of the illness is not yet determined, however, there are instances or conditions that could trigger the onset of disease.
Vasculitis causes
There are two classifications of vasculitis, namely, Primary Vasculitis and Secondary Vasculitis. Primary vasculitis is when there is an inflammation of the blood vessels but the cause is unknown. On the other hand, Secondary vasculitis is referred to as the swelling of the blood vessel due to another medical condition or disease.
Below are some common examples of underlying health conditions that can give rise to secondary vasculitis:
- Hepatitis C and multiple myeloma cause cryoglobulinemia. This is a condition wherein the proteins of the blood form precipitates if the temperature of the body drops below 37 degrees Celsius, returning only to their normal consistency once the body temperature is warmed up to the normal body temperature. When this happens, the blood vessels get stretched when the precipitates form, thereby resulting to vasculitis.
- Diseases brought about by a damaged immune system could also cause vasculitis. These include rheumatoid arthritis wherein there is an inflammation commonly found in the joints. The inflammation could press the blood vessels causing them to wear out resulting to vasculitis.
- Allergic reaction to drugs. If you are allergic to even one of the components of the medicine, a possible response of the body could include the inflammation of the blood vessels.
- Cancers that involve the cells of the blood, such as lymphoma and leukemia. The normal flow and consistency of the blood would be affected, which could then lead to the blood vessels getting overworked and stretched, therefore resulting to inflammation or vasculitis.
Signs and symptoms of Vasculitis
The symptoms of vasculitis highly depend on which part of the body is affected by the condition. However, the most common symptoms and indicators include fever, poor appetite, sensation of weakness or numbness, pain in the muscles and joints, weight loss and tiredness. If these symptoms become apparent and persist, make an appointment with the doctor right away to properly check and correctly diagnose the condition.
Diagnosis of Vasculitis
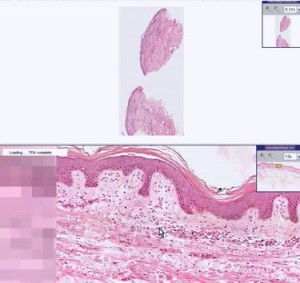
The first thing the doctor would do is to conduct a physical assessment of the patient. He or she would observe the site where the vasculitis might be present and then make inquiries about the patient’s medical history. Diagnostic tests such as biopsy and angiography would be performed in order for the doctor to evaluate the extent and severity of the disease and formulate the most suitable treatment option. Biopsy is a test wherein a piece of tissue from the affected body part is obtained to examine it closely; while angiography is an x-ray wherein a certain dye is used in order to detect any abnormalities in the blood vessels. Urine test and blood test might also be ordered to see if there is any sedimentation found in the blood as a result of vasculitis.
Vasculitis Treatment
When vasculitis and its severity have been confirmed, the best treatment option can be tailored for the specific needs of the patient. The most common treatment for the illness is the use of corticosteroids such as methylprednisone and prednisone. These are available in oral and intravenous dosage forms. If the case of the disease is still mild, the doctor would typically prescribe oral corticosteroids. If the condition is already severe, the doctor would advise the patient to be hospitalized for closer monitoring and intravenous corticosteroid would be administered.
If the vasculitis is secondary to a main disease such as arthritis and cancer, the doctor would treat the main disease first. For cancer, chemotherapy is the most advisable treatment option method.
Vasculitis can be life threatening when not given immediate medical attention. It could develop into an aneurysm, which if not treated promptly, could burst and bleed out and could cause death. At the first signs of the disease, it would be wise to see a doctor right away so that the best treatment method could be applied in order to prevent further damage. It is also essential that the person should take care of himself/herself after the treatment as recurrence of vasculitis is very possible. One need to have a healthy lifestyle, exercise regularly, and drink the medications the doctor had prescribed. It is also recommended to have regular checkups with the doctor in order to prevent vasculitis from getting worse.
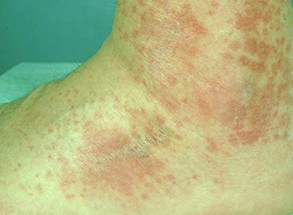
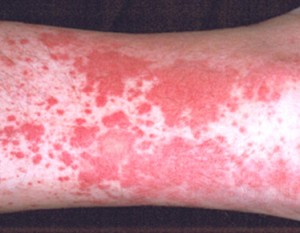
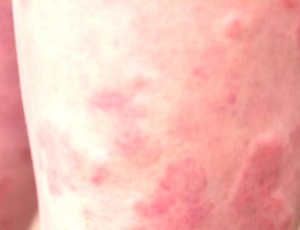
Vasculitis pictures
Here are the pictures of vasculitis, find out how the blood vessels are thickened and the skin develops rash and inflammation