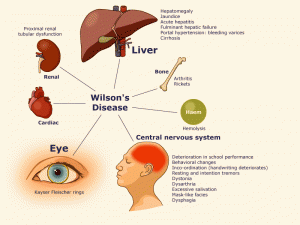
Wilson’s disease is a genetically inherited disorder caused by a mutation in the Wilson disease protein (ATP7B) gene which stops our body from disposing extra copper in our system. Our body’s daily need is at least 1-2 mg of copper per day to stay healthy but too much copper present can also be poisonous. Through Wilson’s disease, copper is retained inside the liver causing injuries to the tissues resulting to the transportation of all extra copper directly into the blood stream and towards the liver, kidney, eyes, brain, and to the other organs. This high copper level in the organs may lead to serious damage that can be life threatening if not treated right away.
Copper is a metal that is a very important cofactor of most proteins in our body system. An average diet can provide substantial amounts of our daily copper needs. copper is absorbed in the small intestine and transported through the blood stream towards the liver. The liver utilizes this for our body’s daily metabolic needs.
Genetics behind Wilson’s Disease
ATP7B is a gene responsible for transporting copper. It is a member of ATPase transport family that encodes a protein and functions as a monomer or an exporter of copper out from the cells. A mutation in the gene located at chromosome 13 is responsible in developing such disease. As of now, 300 mutations have been identified associated with Wilson’s disease.
A gene called PRNP which produces prion protein that activates in the brain and in other tissues is believed to be involved in the distribution of copper. A normal variation of this gene with ATP7B can help delay the course of the disease and affect the symptoms that have developed.
This condition can be inherited through an autosomal recessive pattern which means the disease is only inherited if both parents are carriers of bad genes. But for people with no family history of Wilson’s disease it doesn’t exclude them from acquiring such disease. Most patients are known to have no family history of the said condition.
Causes
The main cause of Wilson’s disease is the genetic mutation of ATP7B that leads to the buildup of copper inside the body. Most people usually eat food more than they could handle and get too much copper than what the body actually needs; this excess copper is excreted into bile. People who inherited bad genes are most at risk of developing such disease if they do not particularly watch their food intake. The copper build up can cause serious damage and may sometimes have irreversible harm which in time can impair other organs too.
Signs and Symptoms
Wilson’s disease will first attack the liver and then the central nervous system or sometimes even both. Usually this type of disease mimics other conditions that often lead to confusion or mix-up with other disorders. Signs and symptoms may vary depending on the part of the body affected by the disease.
Buildup of copper in the liver can cause liver disease. Though acute liver failure rarely occurs, most patients may develop such signs and symptoms associated with chronic liver disease:
• Swelling in the liver or spleen
• Yellowing of skin and eyes or jaundice
• Fluid buildup mostly in legs and abdomen
• Fatigue
• Easily bruised
• Increased tendency of bleeding
• Portal hypertension
• Spider naevi
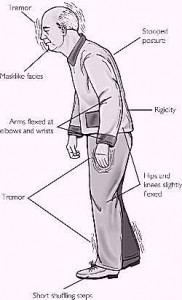
When copper buildup reaches the central nervous system, this condition would result to development of neuropsychiatric symptoms. Nearly half of all Wilson’s disease patients are suffering from neurological and psychiatric problems. Neurological symptoms include:
• Speech problems
• Ataxia or lack of coordination
• Dystonia, a condition in which a part of the body involuntarily twists and executes repetitive movements
• Seizures
• Migraines
• Muscle stiffness
• Cognition that comes in two categories; Frontal lobe disorder includes impaired judgment, impulsivity, apathy, promiscuity, and executive dysfunction; and Subcortical dementia includes slow thinking, executive dysfunction, and memory loss
• Behavioral changes
• Depression
• Anxiety
• Psychosis
Other symptoms manifested if other organ systems are afflicted:
• Eyes: Kayser Fleischer rings which may or may not occur and are only visible through slit lamp examination; sunflower cataracts; green or brown pigmentations in the lens capsule. These symptoms do not show any significant threat to vision loss.
• Kidneys: Renal tubular acidosis is a disorder which may lead into conditions like nephrocalcinosis, weakening in the bones, and aminoaciduria.
• Heart: Cardiomyopathy which rarely happens and may lead into heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias
• Hormones: infertility; habitual abortion; hypoparathyroidism which may lead to low calcium level
Other signs and symptoms include:
• Anemia
• Slow blood clot
• Low platelet
• High levels in uric acid, amino acids, protein, and carbohydrates presence in the urine
• Arthritis
• Premature osteoporosis
Complications
Complications brought by Wilson’s disease include:
• Cirrhosis or scarring of the liver
• Liver failure
• Liver cancer
• Persistent neurological difficulties
• Kidney problems
• Severe brain damage
• Death
Tests and Diagnosis
Patients who have the symptoms stated above most likely have Wilson’s disease and those who have family history of the illness are considered suspects as well. Though it’s hard to link such symptoms to Wilson’s disease, a combination of both physical examination and laboratory test is done to help confirm the disease to avoid misdiagnosis. Laboratory tests include:
• Urine and blood tests
• Brain scans
• Eye exam
• Liver tissue sample for testing
• Genetic testing
• Urine and blood copper level
• Liver biopsy
Drugs and Treatment for Wilson’s Disease
Wilson’s disease is incurable which means it needs lifelong medications to help control copper build up inside the body.
Medical treatments are available to help remove excess copper or prevent copper from being absorbed especially during meals. Medications like penicillamine and trientine hydrochloride help release the copper from the affected organs. Pregnant women are advised to take low dosage of these medications to help reduce risk of birth defects.
Physiotherapy is given to patients with neurological problems and liver transplant is performed for patients with numerous risks complications who failed to respond to various medical treatments. In general, a person with Wilson’s disease is advised to have a low-copper diet specifically avoiding mushrooms, chocolates, nuts, liver, dried fruit, and shellfish. The earlier the disorder gets detected and treated, the longer the person can enjoy a good healthy life.