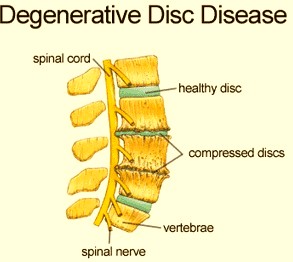
Degenerative disc disease is a name used to refer to certain changes in the spinal discs when a person ages, hence it is not really an illness. The spinal discs are compressible discs which are soft and attach each of bone in the vertebrae to each other to make up the entire spine. The discs act as shock absorbers allowing for the bending, twisting and flexing of the spine.
The degenerative disc disease happens anywhere on the spine although oftentimes it happens on the discs located on the cervical region or the neck and the lumbar region or the lower back. Any changes in the discs will result to pain on certain parts of the body. The following are some irregularities in the spine that cause pain:
• Herniated disc – an irregular swelling or the bursting of the spinal disc. Here is more information on herniated cervical disc symptoms, treatment.
• Osteoarthritis – the cessation of the cartilage which are the ones protecting and cushioning the joints. Find out more information about the symptoms and treatment of osteoarthritis
• Spinal stenosis – the condition in which the spinal canal is narrowed
The conditions stated above exert pressure on the nerves and the spinal cord. This in turn causes pain to certain body parts. If left unmanaged, they may affect normal functioning of the nerves.
Causes of Degenerative disc disease
As mentioned before, degenerative disc disease is not a disease. This condition naturally happens to people, particularly when they are aging as this is considered a part of the cycle. The changes one could anticipate are:
• Small cracks or tears in the capsule or annulus fibrosus, which is the outer layer of the spinal disc. The nucleus pulposus, the jelly-like substance within the disc, could seep through the cracks and tears on the outer shell. This leads to swelling of the disc, rupture and even broken disc that release fragments.
• The nucleus pulposus may lose fluid or dry up due to aging. When this happens it reduces the ability of the discs to absorb impact, resulting to rigidity of the spine. Because there is loss of fluid in the inner layer, the disc will become thinner, resulting to shorter distance between vertebrae.
Individuals who do heavy work and repetitive lifting of heavy loads, those who smoke and those who are overweight have higher chances of developing degenerative disc disease. An accident that leads to injury to the spine may catalyze the progress of this condition.
The stability of the spine degenerates when the space and the padding of the vertebrae grow thinner. The body reacts by creating osteophytes or bone spurs. These osteophytes exert pressure on pressure on the nerve roots and the spinal cord resulting to pain and eventual nerve function abnormality.
Degenerative Disc Disease Symptoms
The symptoms of degenerative disc disease may be neck pain or back pain but overall they differ from one person to another. Majority of the people with this condition feel no pain while others who have the same disc damage to the spine may have serious pain that can impede their daily functioning. Likewise, the location of the pain highly depends on which disc is affected. If the disc located in the neck is the one with the problem, it may result to arm pain or neck pain; while if the affected disc is at the lower back it will result to back pain, leg pain or buttocks pain. The pain may grow worse during activities such as twisting, turning the back or neck, reaching up or bending over. It may begin when one is involved in a serious injury like a car incident; mild injury like a fall from low height or normal movement which highly happens when one bends over on the floor to pick up something. There are also other cases where pain happens for no reason at all.
Diagnosis
The basics procedures are done to diagnose degenerative disc disease. First, the doctor will interview you about your medical history and conduct physical examination. Depending on how severe the symptoms are, you may need to do a series of tests. Oftentimes, he/she will also inquire about your family’s medical history. Other questions include past or recent injuries, illnesses and symptoms; previous treatments, medications, habits or activities that may result to pain in the legs, buttocks, back, arms or neck. The physical examination for degenerative disc disease involves:
• Checking the scope of motion of the affected area and the movement which causes pain.
• Confirming the existence of any tingling sensation, numbness or weakness on the affected area as well as any changes in reflexes.
• Checking for other conditions including infection, tumors or fractures.
X-ray, CT scans or Magnetic Resonance Imaging may be ordered if the preliminary assessments reveal no conclusive evidence of any serious condition.
Degenerative Disc Disease Treatment
Some home remedies are employed to help relieve pain, such as applying heat or warm compress, putting ice or cold compress. Putting cold compress is recommended for the first 48 hours after symptoms appear to reduce any swelling and pain. Heat is applied after this period to initiate proper blood circulation to promote healing. The use of medications such as acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs which includes aspirin or naproxen sodium like Aleve, may be prescribed by the doctor. Aspirin is not recommended to be given to patients under 20 years of age to prevent the risk of acquiring Reye syndrome. Tylenol, an example of acetaminophen helps relieve the pain. Doctors may prescribe stronger medications to you if the above mentioned are not effective.
If the conservative treatment options do not work for you, you should seek professional medical aid and other alternatives. More treatments are available for degenerative disc disease, although these depend whether the damaged disc is the result of a previous or recent condition such as spinal stenosis, herniated disc or osteoarthritis. Doctors may recommend patients to do stretching or strengthening exercises and undergo physical therapy. There are other cases where surgery is needed when the condition is more severe. The surgery usually includes removing the disc that is damaged. Other cases involve permanently joining or fusing the bone in order to protect the spinal cord. Artificial discs are oftentimes recommended to replace the removed discs.
Awsome site! I am loving it!! Will come back again. I am taking your feeds also.