Splenic flexure syndrome refers to a digestive condition which causes spasm of the splenic flexure occurring in the colon. Trapping of gas is what leads to the spasm. The abdominal pain and discomfort that is endured is debilitating and intense and can be compared to that experienced during a cardiac arrest. This kind of digestion condition results in gas that is extremely higher than normal levels.
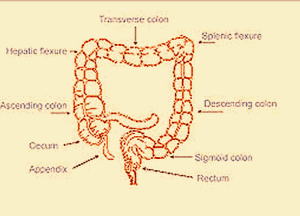
The splenic flexure is situated next to the spleen and a section of the large intestine or colon. It is a quick bend in the upper left abdomen, which alters direction from horizontal to vertical. It does not possess a main source of blood supply and therefore relies on the terminal branches of inferior mesenteric artery and superior mesenteric artery. The splenic flexure is situated between the descending and transverse colon.
Symptoms of splenic flexure syndrome
Some of the signs and symptoms of splenic flexure syndrome are as follows:
- Individuals affected by biliary dyskinesia may experience agonizing pain which is almost akin to a heart attack
- The most common symptom of splenic flexure syndrome is pain in the upper left abdomen
- When one taps the upper abdomen, one can hear a drum like sound
- Occurrence of obvious mass
- The abdominal pain may be felt when twisting the upper body or bending, and is particularly triggered while sitting down
- The upper part of abdomen experienced distention and is tender to touch
Other symptoms which are common to other conditions as well include:
- Constipation
- Fever
- Diarrhea
- Colon spasm
- A quick heart rate
- Occurrence of increased gas
- Abdominal cramps
- Bloating
Splenic Flexure Syndrome Causes
Some of the causes of splenic flexure syndrome are discussed below:
- Undigested food can result in increased gas, because improperly absorbed and digested food is broken down by bacteria present in the large intestine and gas is produced as a byproduct during the process
- Diarrhea and gas production may be caused by food poisoning, which may result from bacterial infection like E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, etc.
- Diarrhea and abdominal bloating may also result from short-chained carbohydrates, which pull water to the intestinal lumen from the intestinal vessels post ingestion, and create large quantities of gas. Prunes, wheat, brussel sprouts, legumes and apples are examples of foods categorized as short chained carbohydrates
- Adhesion of the abdomen that occurs post abdominal surgery may block food passage and blood supply leading to abdominal bloating and pain
- Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disorder that begins in the rectal region and over time may also affect the complete large intestine. The underlying presence of ulcerative colitis can increase the risk to developing splenic flexure syndrome
- Aerophagia or swallowing of air results in entry of air into the esophagus. This may occur when chewing gum, rapidly drinking or eating, nasal blockage, breathing through the mouth or hyperventilation.
- Crohn’s disease is another inflammatory bowel disorder majorly affecting the intestines and often occurring in the mouth to the end part of the rectum. Patients experience persistent inflammation of the GI tract and in any part of the digestive tract
- Serious diseases like pancreatitis or cancer which result in obstruction may also lead to development of splenic flexure syndrome
- It can also be caused due to infections like amoebiasis or tuberculosis
- Abnormalities in contractions to facilitate automatic movement of food through the digestive tract can result in trapping of gas air pockets
Splenic Flexure Syndrome Treatment
- The treatment of splenic flexure syndrome is aimed at managing the symptoms with medications. The signs of intestinal spasm can be relieved with anticholinergic medications. The disorder has been found experience improvement with antispasmodics. Dicyclomine alleviates pain and fecal urgency
- The distinctive pain associated with splenic flexure syndrome can be reduced by passing of stool and gas
- Avoidance of hunching and a good posture can aid in the prevention of air traps
- Avoidance of air swallowing is one of the best ways to decrease or eliminate gas production. Doctors suggest the intake of probiotic supplements before meals. Healthy digestion is aided by slow and thorough chewing of food and eating the right way.
- The modification of diet can contribute in minimizing bouts of abdominal pain. Foods that can result in gas should be avoided so as to prevent the exacerbation of existing symptoms
A proper diet for patients of splenic flexure syndrome includes the following:
- Sodium intake has to be reduced along with increased consumption of potassium. Potassium drives water away from cells while sodium takes in water. Banana and root vegetables are rich in potassium
- A fiber diet or supplements can also help in easing of splenic flexure syndrome symptoms
- Lactose intolerant individuals should avoid lactose or dairy products. All the different types of food allergies have to be identified and should be completely avoided.
- Splenic flexure syndrome patients affected by constipation should drink plenty of water and fluids.
Fantastic items from you, man. I’ve take note your stuff prior to and you are simply extremely fantastic. I really like what you’ve bought here, certainly like what you’re stating and the way wherein you say it. You make it enjoyable and you still care for to stay it smart. I can not wait to learn much more from you. This is really a great web site.